39 dosage calculations from medication labels
18 Heart Failure Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs 08.07.2022 · Careful control of the dosage of beta-blockers can improve patient status by improving LV ejection fraction, increasing exercise tolerance, slowing HF progression, reducing the need for hospitalization, and prolong survival (Butler et al., 2006; Barrese et al., 2013). Side effects to look out for include worsening HF symptoms, hypotension, fatigue, and bradycardia. Oral Drug Dosage Calculator - Liquid Solution Syrup × Q (quantity) X (amount) = 500 milligram 250 milligram ×5 milliliter X (amount) =10 milliliter Description: This calculator determines the volume of liquid, solution or syrup to be administered to the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine.
6.2 Safe Medication Administration – Clinical Procedures for Safer ... Be diligent in all medication calculations. Errors in medication calculations have contributed to dosage errors, especially when adjusting or titrating dosages. Avoid reliance on memory; use checklists and memory aids. Slips in memory are caused by lack of attention, fatigue, distractions. Mistakes are often referred to as attentional ...
Dosage calculations from medication labels
Drug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide - KnowledgeDose What is the correct dosage on the label? Take 800 units (0.4ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.8ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.6ml) once daily Take 800 units (1ml) once daily 69 Likes About KnowledgeDose Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? If you want to calculate the dose of a medication, you need to use the following equation: Dose = Weight × Dosage Dose = W eight × Dosage. Where: Weight — Patient's weight, expressed in kg or lb. It is very important that you input an accurate result; Dosage — Prescribed amount of drug in mg per kg of body weight. Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Step 3: The desired dose is 0.5 mg. Place information with the same label as the preceding denominator into the equation in the numerator to cancel out the unwanted labels. Repeat this step sequentially until all unwanted labels are canceled out. Step 4. Multiply numbers across the numerator, then multiply all the numbers across the denominator.
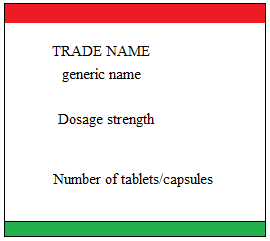
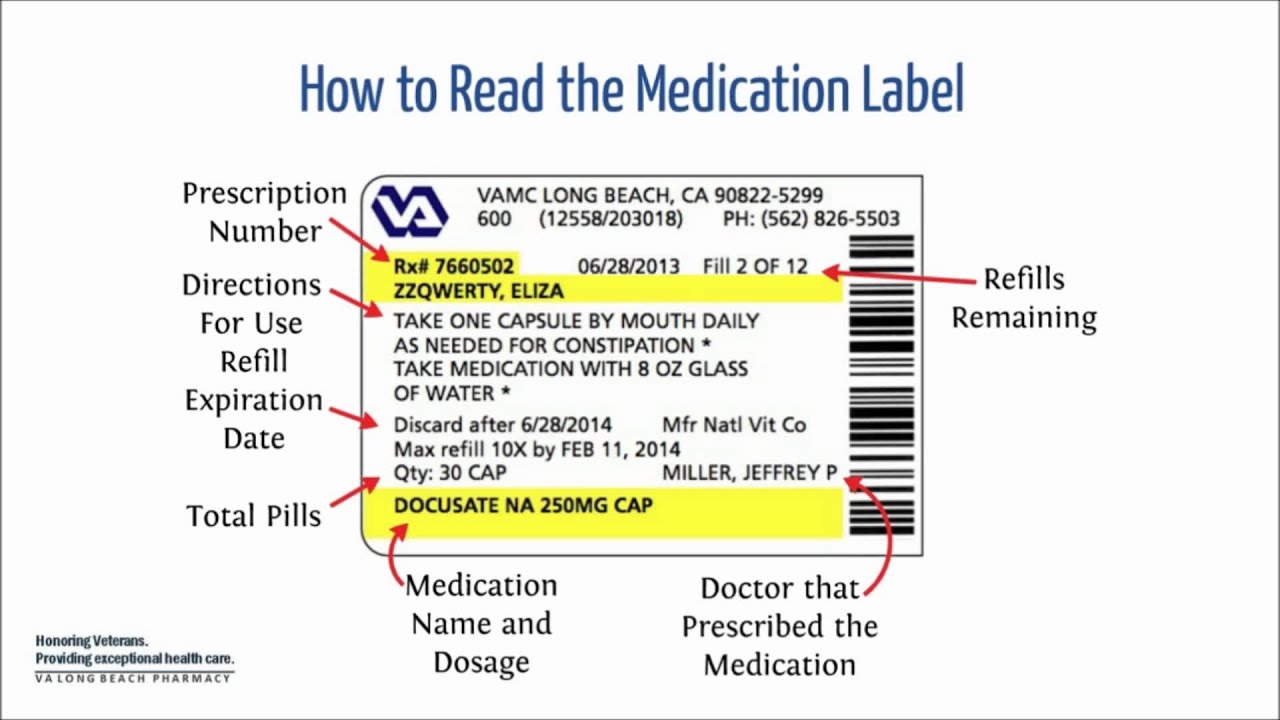
Dosage calculations from medication labels. PDF Formulas for Calculating Medication Dosage - Indian Hills Community College the medication label, and Q (quantity) is the volume in which the dosage strength is available (e.g. tablets, capsules, milliliters). For example: we have an order for Ceclor 0.5 g PO b.i.d. We have available 250 mg capsules. The first thing to do is get like units of measurement. Since we have 250 mg capsules, let's change our ordered dose ... Reading Medication Labels | Basicmedical Key CHAPTER 13 Reading Medication Labels Objectives After reviewing this chapter, you should be able to identify: 1. The trade and generic names of medications 2. The dosage strength of medications 3. The form in which a medication is supplied 4. The total volume of a medication container where indicated 5. Directions for mixing or preparing a drug where necessary 6. Dosage Calculations, 9th edition 9th Edition - amazon.com Dosage Calculations, 9th edition: 9781439058473: Medicine & Health Science Books @ Amazon.com ... Featuring full-color images of drug labels, critical thinking assessments, extensive clinical examples, and a host of interactive supplements, including an accompanying online tutorial, DOSAGE CALCULATIONS, 9th Edition provides the skills needed to master … The administration of medicines | Nursing Times 19.11.2007 · It may require dose calculations, dilutions, information to be gathered on administration rates and compatibilities with other IV solutions, and the use of programmable infusion devices. Moreover the preparation of IV medicines requires the use of an aseptic technique, often in a ward environment that is unsuited for such work. It is imperative that to …
Pharmacology - 10th Edition - Elsevier Prototype drug charts summarize the need-to-know information about key drugs, including dosage, side effects, interactions, and more. Images of current drug package labels reinforce your understanding of text content using relevant, true-to-life learning. Bulleted nursing process summaries relate nursing care to drug therapy in addition to highlighting patient teaching, … Medical Dosage Calculations For Dummies Cheat Sheet Common conversion factors in medical dosage calculations. As a healthcare professional, you have to convert patient weights, fluid volumes, medication weights, and more. Conversion math isn't hard to do as long as you know the basic conversion factors. Here are the most useful ones: Converting lb to kg and kg to lb. lb = kg × 2.2. kg = lb ÷ 2.2 15.4 Checklist for Oral Medication Administration – Nursing Skills Perform necessary calculations to verify correct dosage. The right patient: Check that you have the correct patient using two patient identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth). The right medication (drug): Check that you have the correct medication and that it is appropriate for the patient in the current context. PDF Drug Calculation tutorial - Midlands Tech Ordered Dose of the drug X Drug Strength (how the drug is supplied (ml, tabs, capsules, etc) amount of the drug (mg, mcg, g, mEq, etc) Be sure you set your problem up so you are able to cancel all labels except the one you are solving for. If you are solving for tablets, the tablet label needs to be on top of the fraction (numerator) and it
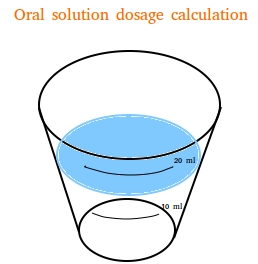
PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Every tenth of a mLis marked on the syringe, and every half mL is labeled; this means that any dosage we plan to measure using a 3 mL syringe should be rounded to the nearest tenth. Dosages between 1-3 mLshould always be measured in a 3 mL syringe. Lisinopril (Prinivil, Qbrelis) | Davis’s Drug Guide Davis’s Drug Guide for Nurses App + Web from F.A. Davis and Unbound Medicine covers 5000+ trade name and generic drugs. Includes App for iPhone, iPad, and Android smartphone + tablet. Handbook covers dosage, side effects, interactions, uses. Davis Drug Guide PDF. Explore these free sample topics: Dosage Calculations Made Easy | Reconstitution Calculation Medication ... Dosage Calculations Nursing Students: This video demonstrates how to solve dosage and calculation problems for reconstitution of medications. I use dimension...
Calculations of Oral Doses | Basicmedical Key Be sure all of the measurements are in the same system and all units are the same. It is preferable to convert to the system of measurement used for the medication on hand. Step 2. Think. Estimate a reasonable amount that should be given. Step 3. Calculate the drug dose with one of the three methods shown. Step 4.
Dosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels - StuDocu Dosage Calculation: Reading Drug Labels Chapter 11. Tarleton State University NURS 3310 Dr. Mary B. Winton. Reading Drug Labels. a. Brand/trade name b. Generic name c. Formulation d. Dosage strength e. Route f. Need prescription or Over -the-counter. Reading Drug Labels and Reconstitution. a. Generic name b. Brand/trade name c. Formulation d ...
ATI Dosage Calculations 3.0: Oral Medications - Quizlet How many capsules should the nurse administer per dose? 2 capsules A nurse is preparing to administer trazodone 25 mg PO at bedtime. Available is trazadone 50 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer per dose? 0.5 tablets A nurse is preparing albuterol 4 mg PO every 6 hr. Available is albuterol syrup 2 mg/5 mL.
Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the milliliters of Augmentin required. Problem 2.) Determine the...
LibGuides: Clinical Calculations: Module 6: Divided Doses and ... Your charge nurse recommends that you use 1.8 ml of sterile water to reconstitute the medication to reduce the volume to be injected. How many ml will you give per dose? SF = 2 g AU = ml per dose Equivalents: 1 g = 1000 mg 400 mg = 1 ml (from the reconstitution directions on the label)
Pharmacy Technician Certification Exam (PTCE): Test Prep ... Sep 30, 2022 · The exam has nine knowledge domains and areas: pharmacology for technicians; pharmacy law and regulations; compounding; medication safety; quality assurance; medication order entry and fill ...
Dosage Calculator - [100% Free] - Calculators.io Here are the steps to follow for using this drug dosage calculator: First, enter the value of your Weight and choose the unit of measurement from the drop-down menu. Then enter the value of the Dosage and choose the unit of measurement from the drop-down menu. For liquid medications, also enter the value of the Medicine Concentration and choose ...
Nursing Pharmacology: Dosage And Calculations Practice Test - RN speak The medication label reads "1,200,000 units per 2 mL." The nurse has determined that the dose prescribed is safe. The nurse administers how many milliliters per dose to the child? a. 0.8 mL b. 1.2 mL c. 1.4 mL d. 1.7 mL 19. Atropine sulfate, 0.6 mg intramuscularly, is prescribed for a child preoperatively.
Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA
Dosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN - Registered nursing Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg How many tablets should be administered daily? In this problem you have to determine how many tablets the patient will take if the doctor order is 125 mg a day and the tablets are manufactured in tablets and each tablet has 250 mg. This problem can be set up and calculated as shown below.
Dosage Calculation Practice Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A patient has an order for Chloromycetin, 500 mg every 6 hours. The drug comes in 250 mg capsules. What would the nurse administer?, A nurse is to administer 150 mg of a drug intramuscularly. The label on the multidose vials reads 100 mg/mL. How much would the nurse give?, A nurse is to administer 30 mg of furosemide (Lasix) to a ...
Pharmacology Calculations and Conversions - Study.com Jan 21, 2022 · These labels should be checked in accordance with the eight rights of administration to ensure that the administration route and dosage are correct before administering the medication.
PDF Drug dosage calculation handout for BSN completion Dosage by weight (with label) 2 Continuous IV med (flow rate or medication delivered) 2 Direct IV (IV push) (with label if possible) 2 Total 20 Recommended text: Olsen, J., Giangrasso, A. & Shrimpton, D. (2015). Medical dosage calculations: A dimensional analysis approach. Boston, MA: Pearson
Dosage (Drug) Calculations Nursing Review- COMPREHENSIVE This is a comprehensive dosage calculation review for nursing students. In this review we will start by working basic metric conversions and then progress to solving more complex dosage calculations. You will learn how to work the following drug calculation problems: Conversions Oral Liquid Medications Capsules and Tablets IV Boluses
Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method The answer seems plausible, so the work is done. 1000/500 x 10/5 = 2, the 2 zeros in 1000 and 2 zeros in 500 can be crossed out since like units in numerator and denominator, leaving 10/5, a much easier fraction to solve, and the answer makes sense. If you multiply a number by a 1, then the number is unchanged.
Nursing Math - Parenteral Injectable Drug Dosage Calculator Parenteral Drug Dosage Calculator For Syringe Liquid Solutions Medicine Injectable Dosage Equations Formulas. Description: This calculator determines the liquid or solution volume to be injected by syringe into the patient. The label on the medicine bottle states the concentration of the medicine. The concentration is the mass of medicine ...
PDF Medication Calculation Examination Study Guide - Los Angeles County ... Label shows 75 - 150 mg/kg per day. Is the physician's order within normal range? Solution: 6 x 75 = 450 mg (minimum dosage per day); 150 X6 = 900 (maximum dosage per day) 24 ÷ 4 = 6 dosages : 300 x 6 = 1800. Answer: Dosage is not within range. IV Calculations • [amount of fluid to be infused] x [drop factor] ÷ minutes to infuse = gtts/min
Pharmacy Dosage Calculations | Pharmacy Math Made Simple! - PharmaFactz Doses are delivered every 5mL - meaning this patient's dose of 15mL comprises three 5mL spoonfuls. 4 times daily dosing for 7 days constitutes 28 doses- again, each dose consists of a 5mL spoonful. 28 doses x 15mL = 420mL of cough medicinemust be dispensed.
Wellbutrin SR (bupropion hydrochloride) dose, indications, … Consider reduced dosage and/or dosage frequency in patients with a CrCl < 90 mL/min; specific recommendations are not available. Bupropion and its metabolites are renally eliminated and may accumulate in patients with renal impairment. Use of Forfivo XL, a 450 mg extended-release tablet formulation, is not recommended in patients with renal impairment because there is no …
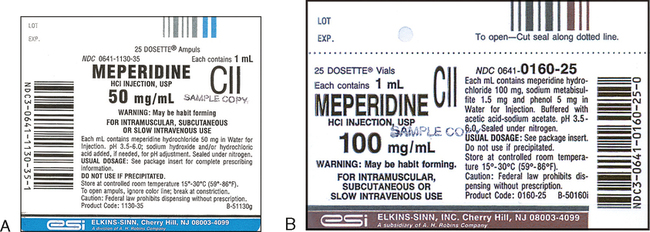
How to Read a Medication Label Nursing Quiz - Registered Nurse RN According to the medication label, what is the dosage strength of this medication? A. 7 g B. 100 mL C. 80 mL D. 350 mg/5 mL The answer is D. Dosage strength is the amount of drug that is in the specific dosage form supplied. 5. How is this medication supplied according to the medication label? A. Capsule B. Injection Solution C. Oral Solution
Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Dosage units: mg This one is a little tricky because the label does not actually state what the units are! However, because mg are the most commonly used units for drug dosages, we are supposed to assume that the 750 on the label means 750 mg.
Drug Calculations: How To Use Dimensional Analysis Step 3: The desired dose is 0.5 mg. Place information with the same label as the preceding denominator into the equation in the numerator to cancel out the unwanted labels. Repeat this step sequentially until all unwanted labels are canceled out. Step 4. Multiply numbers across the numerator, then multiply all the numbers across the denominator.
Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? If you want to calculate the dose of a medication, you need to use the following equation: Dose = Weight × Dosage Dose = W eight × Dosage. Where: Weight — Patient's weight, expressed in kg or lb. It is very important that you input an accurate result; Dosage — Prescribed amount of drug in mg per kg of body weight.
Drug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide - KnowledgeDose What is the correct dosage on the label? Take 800 units (0.4ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.8ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.6ml) once daily Take 800 units (1ml) once daily 69 Likes About KnowledgeDose


























Post a Comment for "39 dosage calculations from medication labels"